Introduction
Automation is revolutionizing the film and television production industry, offering unprecedented efficiency, creativity, and cost-effectiveness.
This document explores various applications of automation through compelling case studies, highlighting the transformative impact on different stages of production.
Pre-Production: Streamlining Planning and Logistics
Automation in pre-production helps optimize critical tasks like script breakdown, scheduling, and budgeting. By automating data entry and analysis, production teams can allocate resources more efficiently and identify potential issues early on.
Case Study 1: Script Breakdown and Budgeting Software
A mid-sized independent film studio adopted an AI-powered script breakdown and budgeting software. This system automatically scanned scripts, identified key elements (characters, props, locations), and generated preliminary budget estimates based on historical data.
| Feature | Traditional Method | Automated Method |
|---|---|---|
| Script Breakdown | Manual reading and annotation, prone to human error | AI-driven analysis, higher accuracy |
| Budget Generation | Manual data entry and calculation, time-consuming | Automated estimation, faster and more consistent |
| Resource Allocation | Intuitive, often reactive | Data-driven, proactive |
This implementation led to a 30% reduction in pre-production time and a 15% improvement in budget accuracy, allowing the studio to take on more projects and allocate resources more strategically.
Production: Enhancing Creative Control and Efficiency
During the production phase, automation tools range from advanced camera robotics to intelligent lighting systems, enabling filmmakers to achieve complex shots with precision and consistency.
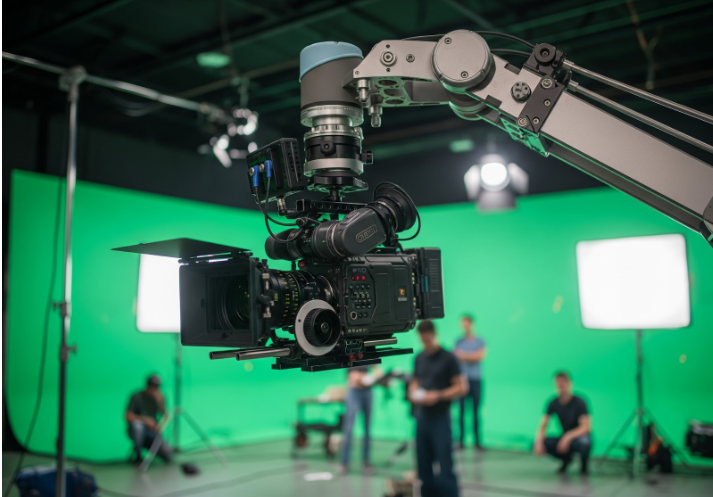
Case Study 2: Robotic Camera Systems for Dynamic Shots
A popular TV drama series utilized robotic camera systems for its fast-paced action sequences. These systems, programmed with precise movements, allowed for repeatable, complex camera maneuvers that would be difficult or impossible with traditional manual operation.
The use of robotics minimized the need for multiple takes, resulting in significant time savings on set. Furthermore, the precision offered by these systems ensured visual continuity across different shooting days. This also enabled the crew to focus on creative aspects rather than the mechanics of camera operation.
Post-Production: Accelerating Editing and Visual Effects
Automation in post-production significantly speeds up workflows in editing, color grading, and visual effects, while maintaining high-quality output.
Case Study 3: AI-Assisted Video Editing and Color Grading
A documentary production company integrated AI-assisted editing software that automated initial cuts and identified optimal color grading settings. The AI analyzed footage for pacing, narrative flow, and visual consistency, providing editors with a strong starting point.

| Task | Traditional Method | Automated Method |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cut | Manual assembly, time-consuming | AI-generated initial cuts, faster |
| Color Grading | Manual adjustments, subjective | AI-suggested settings, more consistent |
| Workflow Efficiency | Linear and sequential | Parallel and iterative |
This automation reduced the overall post-production timeline by 25%, allowing the company to meet tighter deadlines and increase its output capacity.
Conclusion
The case studies presented demonstrate the tangible benefits of automation in film and TV production.
From optimizing pre-production planning to enhancing on-set efficiency and accelerating post-production workflows, automation is proving to be an indispensable tool.
As technology continues to evolve, we can expect further innovations, including more sophisticated AI for content creation, virtual production environments, and fully automated remote production facilities. The industry is on the cusp of a new era, where human creativity is amplified by intelligent automation.