Verified Intelligence: December 2025
Boardroom Ready
How Generative AI is Disrupting Animation Production Pipelines 2026 is not merely a technical evolution; it is a clinical restructuring of the animation cost-basis and recoupment speed. As we enter 2026, the primary friction is the lethal “Data Deficit” found in legacy outsourcing models that fail to track real-time AI-ready capacity in Sovereign Hubs. By weaponizing vertical AI for automated storyboarding, procedural world-building, and infinite localization, studios are de-risking their slates against the 20% margin leakage typically lost to unverified vendor inefficiencies. This strategic pivot transforms the “Animation Slump” into an “Insider Advantage,” where authorized AI stacks protect IP chain-of-title while accelerating the path to profitability by up to 14 months.
⚡ Executive Strategic Audit
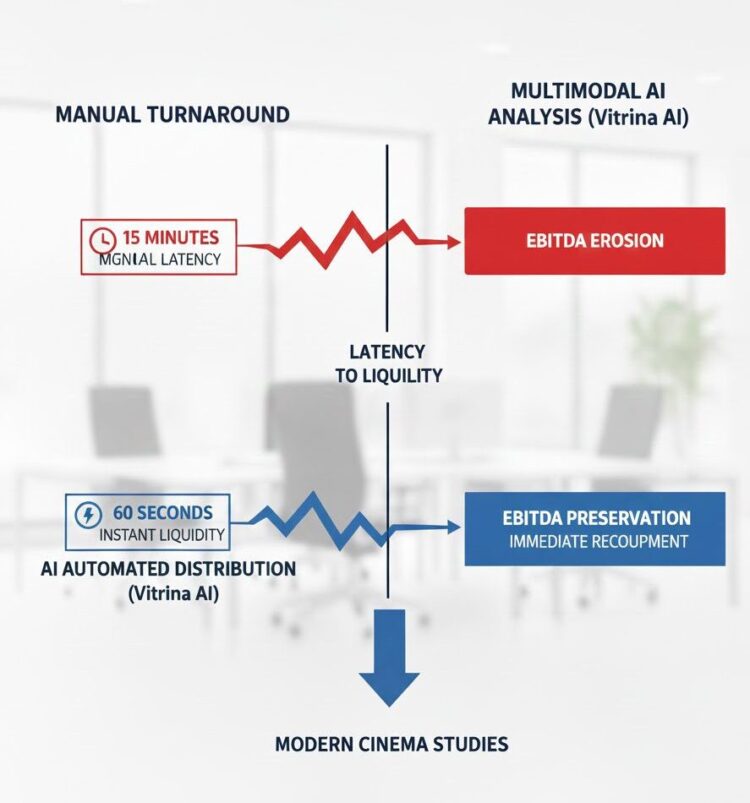
EBITDA Impact
35% Reduction in Pre-Production Burn-Rate
Recoupment Cycle
Accelerated Global Release via AI Lip-Sync
Your AI Assistant, Agent, and Analyst for the Business of Entertainment
VIQI AI helps you plan content acquisitions, raise production financing, and find and connect with the right partners worldwide.
- Find active co-producers and financiers for scripted projects
- Find equity and gap financing companies in North America
- Find top film financiers in Europe
- Find production houses that can co-produce or finance unscripted series
- I am looking for production partners for a YA drama set in Brazil
- I am looking for producers with proven track record in mid-budget features
- I am looking for Turkish distributors with successful international sales
- I am looking for OTT platforms actively acquiring finished series for the LATAM region
- I am seeking localization companies offer subtitling services in multiple Asian languages
- I am seeking partners in animation production for children's content
- I am seeking USA based post-production companies with sound facilities
- I am seeking VFX partners to composite background images and AI generated content
- Show me recent drama projects available for pre-buy
- Show me Japanese Anime Distributors
- Show me true-crime buyers from Asia
- Show me documentary pre-buyers
- List the top commissioners at the BBC
- List the post-production and VFX decision-makers at Netflix
- List the development leaders at Sony Pictures
- List the scripted programming heads at HBO
- Who is backing animation projects in Europe right now
- Who is Netflix’s top production partners for Sports Docs
- Who is Commissioning factual content in the NORDICS
- Who is acquiring unscripted formats for the North American market
How Generative AI is Disrupting Animation Production Pipelines 2026: Procedural Disruption
Behind closed doors, the conversation is actually about the industrialization of the creative soul. In practice, this usually means that the “traditional” three-year animation cycle is being compressed into an eighteen-month sprint. The industry talks about “stylized rendering,” but producers are feeling the relief of weaponizing Authorized AI to handle the heavy lifting of procedural environment generation and lighting. By the time a project hits the post-production phase in 2026, AI has already synthesized the visual discord between diverse regional assets, ensuring a day-and-date global release is financially viable.
The “Timing Trap” in animation is the lethal cost of static storyboarding. Legacy pipelines require months of manual iteration; however, in 2026, AI-driven pre-visualization allows CXOs to “see” the final EBITDA of a project before a single frame of high-cost rendering occurs. This is the Insider Advantage: using real-time deal data and production slates to find studios like Toonz Media Group or MARZ that have already integrated these autonomous stacks into their core offering. We are moving from a world of “per-frame” costs to a world of “per-intelligence” value, where the margin is protected by the speed of technical execution.
LeaderSpeak Insight: Jayakumar P, CEO of Toonz Media Group, notes that the integration of AI tools is essential for market adaptation and the preschool audience shift. This de-risks How Generative AI is Disrupting Animation Production Pipelines 2026 by accelerating market expansion and enabling diverse applications of animation in real-time.
Sovereign Hub Arbitrage: The Rise of AI-First Animation Studios
The capital reality of 2026 is that the center of animation gravity has shifted to Sovereign Content Hubs. Locations like India (APAC), Brazil (LATAM), and Saudi Arabia (MENA) are no longer just “service centers”—they are the technical architects of the global supply chain. These hubs are weaponizing aggressive local tax incentives (like the 40% India cash rebate) and combining them with state-of-the-art AI infrastructure. If your sourcing list does not include 30% representation from these regions, your pipeline is structurally uncompetitive.
Let’s be candid: the “West-to-East” export model is dead. These regions are now “Exporting to the World” using Infinite Localization. A Korean animation studio can now produce a show that feels natively Brazilian on day one, thanks to AI-powered, emotionally-synchronized visual dubbing. This de-risks the global rollout by ensuring cultural resonance at the Apex of Engagement. The data deficit in Western studios—relying on static, 6-month-old vendor reports—is being filled by real-time intelligence from platforms like Vitrina, which tracks the verified capacity of these AI-first survivors.
Authorized IP Protection: Avoiding the ‘Timing Trap’ of Scraped AI
Here is where the margin disappears: using unauthorized, “scrapable” AI tools that lack a clean chain-of-title. In 2026, Authorized AI is the only way to protect IP integrity. The transition from “open-source” risks to multi-billion dollar licensed training deals—modeled after the Disney/OpenAI handshake—is the clinical standard for studio survival. CFOs are now auditing animation budgets to ensure that every AI-generated asset is backed by a verified license, de-risking the project from future copyright litigation that could sink a $50M slate.
The “Data Trust Deficit” is real. Senior executives must pivot to Weaponized Distribution, where content is licensed to rivals post-windowing to maximize ROI, but this only works if the IP is airtight. By using real-time mapping of 150,000+ companies, producers can identify which vendors in the APAC and MENA hubs have secure, “Authorized AI” voice and visual stacks. This de-risks the entire production cycle and accelerates the recoupment speed by ensuring the content is ready for immediate licensing across all streaming and theatrical windows.
How Generative AI is Disrupting Animation Production Pipelines 2026: The Strategic Path Forward
The industry has entered a structural metamorphosis where the “Insiders” are those who treat data as weaponry. To survive 2026, your animation pipeline must move beyond the “Walled Garden” model and embrace a data-driven science of partner discovery and procedural automation. The fragmentation paradox is your opportunity: while others struggle with opaque networks, you will use real-time intelligence to unlock the highest-margin production hubs on the planet.
The Bottom Line Animation production in 2026 is a race for recoupment speed. Deploy Authorized AI and Sovereign Hub arbitrage immediately to protect your EBITDA and weaponize your distribution slates against the fragmentation of the global market.
Deploy Intelligence via VIQI
Select a prompt to run a real-time animation supply chain audit:
Find animation studios in APAC specializing in UE5 AI pipelines.
Map M&A history of AI-first animation boutiques in LATAM.
Identify co-pro partners in India for adult animation with AI.
Filter partners with Authorized AI lip-sync stacks.
Which animation hubs in MENA offer 40%+ rebates for AI content?
Monitor competitive slates for AI-driven studios in Korea.
Insider Intelligence: How Generative AI is Disrupting Animation Production Pipelines 2026 FAQ
How does Generative AI accelerate the animation recoupment cycle?
By compressing the pre-production phase and automating procedural assets, AI reduces total production time by up to 50%. This allows studios to release content earlier and activate licensing windows, protecting EBITDA from long-term capital burn.
Why are Sovereign Hubs critical for AI-first animation slates?
Hubs like India and Brazil offer clinical arbitrage: deep technical expertise in AI pipelines combined with 40%+ cash rebates. This de-risks the supply chain by providing high-end capacity at a lower net cost than traditional Western studios.
What is the risk of using unauthorized AI in animation production?
Unauthorized AI creates a lethal chain-of-title liability. Without verified licensing (Authorized AI), studios face the risk of IP injunctions and the total loss of distribution rights, making a project unmonetizable in the global market.
How can VIQI help source AI-ready animation vendors?
VIQI weaponizes real-time data to find studios currently active in AI-driven projects. Prompts like “Find animation studios in APAC specializing in UE5 AI pipelines” bypass the ‘Timing Trap’ of static databases, providing immediate access to verified capacity.